Catatonia
Catatonia used to be defined as a disorder of its own but this is no longer the case in DSM V. It is instead a feature of multiple psychiatric and non-psychiatric disorders. It can commonly be seen in mood disorders such as depression and bipolar disorders but also in schizophrenia.
Catatonia is defined as having 3 or more of the following set of symptoms in each subtype:
- Types
- Retarded catatonia
- Stupor
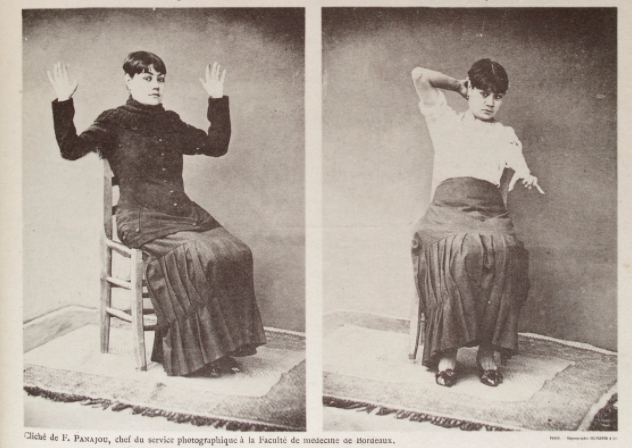
- Catalepsy (waxy flexibility)
- Can place patients in any position and they get stuck in this new position for hours to days

- Mutism
- Negativism
- Excited catatonia
- More activity, saying, doing
- Stereotypy
- Repetitive behaviour
- Agitation or grimace
- Echolalia
- Patient copying what you say
- Echopraxia
- Patient copying what you do
- Retarded catatonia
- Diagnosis
- Clinical
- Administer lorazepam (short acting IV benzos)
- If the patient is back to normal = diagnosis confirmed
- Treatment
- IV lorazepam
- Malnutrition because they stop eating
- Trend albumin and consider enteral nutrition
- Administer low molecular weight heparin or pneumatic compression devices
- Due to reduced movement
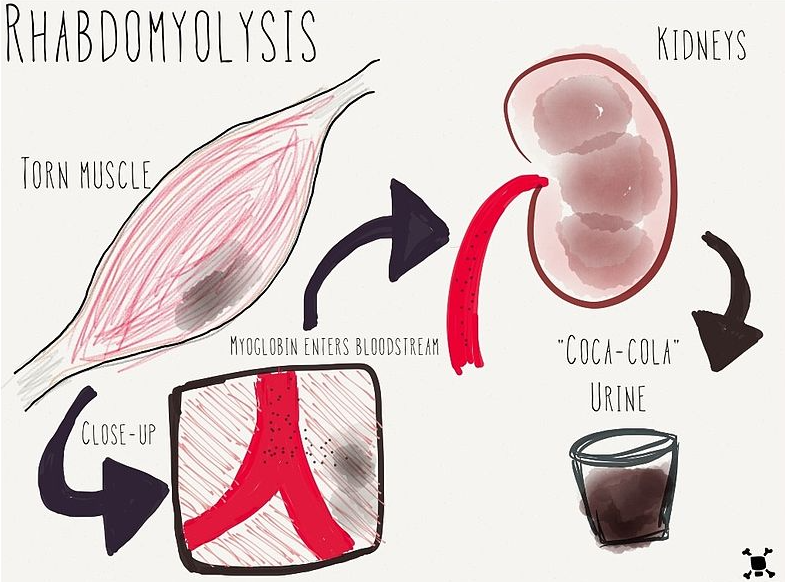
- Check for elevated CK and decreased kidney function
- Risk of rhabdomyolysis if they haven't moved around
Malignant catatonia
Malignant catatonia is a subtype of catatonia. The symptoms are exactly the same as catatonia from other causes.
- Symptoms
- Rigidity
- Lead pipe rigidity with contracted muscles and shaking
- Elevated CK due to extended muscle contraction and the lack of movement
- Autonomic dysfunction
- Elevated heart rate
- Elevated blood pressure
- Elevated fever (>40C)
- Rule out infectious causes
- Rigidity
- Causes
- Psychiatric disease present
- Not caused by medications
- Treatment
- Same as retarded or excited catatonia
- IV lorazepam
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Caused by dopamine antagonists - antipsychotics.
- Symptoms
- Rigidity
- Lead pipe rigidity with contracted muscles and shaking
- Elevated CK due to extended muscle contraction and the lack of movement
- Autonomic dysfunction
- Elevated heart rate
- Elevated blood pressure
- Elevated fever (>40C)
- Rule out infectious causes
- Hyporeflexia
- Decreased or normal bowel sounds
- Rigidity
- Causes
- Psychiatric disease often present
- Patient on antipsychotics
- Diagnosis
- Patient on antipsychotics and has the symptoms above
- Treatment
- Stop the antipsychotics
- Use dantrolene to prevent rhabdomyolysis
Serotonin syndrome
Caused by serotonergic agents - serotonin excess.
- Symptoms
- Not rigidity
- Hypertonicity or hyperreflexia instead of rigidity
- Elevated CK due to extended muscle contraction and the lack of movement
- Autonomic dysfunction
- Elevated heart rate
- Hyperactive bowel/diarrhea
- Elevated blood pressure
- Elevated fever (>40C)
- Rule out infectious causes
- Hyperreflexia
- Dilated pupils
- Not rigidity
- Causes
- Psychiatric disease present - usually mood or anxiety
- Patient on SSRIs or MAO inhibitors
- Diagnosis
- Patient on SSRIs/MAOI's and has the symptoms above
- Treatment
- Stop the SSRIs or MAOI's
Malignant hyperthermia
This will occurs in the OR under anesthesia.
- Symptoms
- Rigidity
- Lead pipe rigidity with contracted muscles and shaking
- Elevated CK due to extended muscle contraction and the lack of movement
- Autonomic dysfunction
- Elevated heart rate
- Elevated blood pressure
- Elevated fever
- Rule out infectious causes
- Rigidity
- Causes
- Not a psychiatric cause
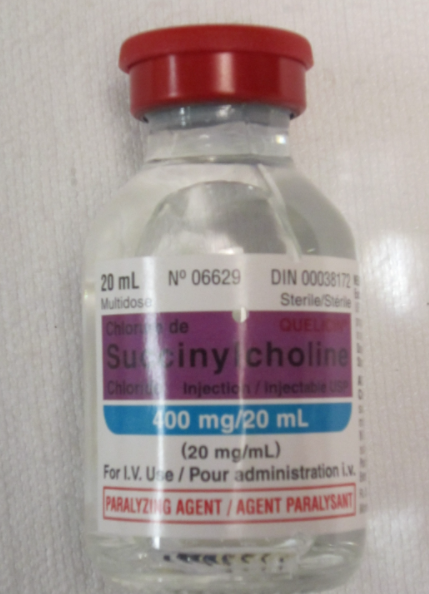
- Certain anesthetics (Succinylcholine or halothane gas common trigger)
- Diagnosis
- Ask for family history of reaction to anesthesia before the procedure
- Treatment
- Ice baths
- Dantrolene = postsynaptic muscle relaxant
All information provided on this website is for educational purposes and does not constitute any medical advice. Please speak to you doctor before changing your diet, activity or medications.