Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
PTSD is a disorder that wasn't properly recognized as a real psychiatric problem up until the Vietnam war. PTSD is one of those disorders that benefits from early treatment with shorter duration and less severe symptoms.
- PTSD
- Life-threatening stressor leading to a disorder
- Severity depends on the stressor and its proximity to the patient
- Furthermore, certain people are more vulnerable to PTSD
- Stressor types
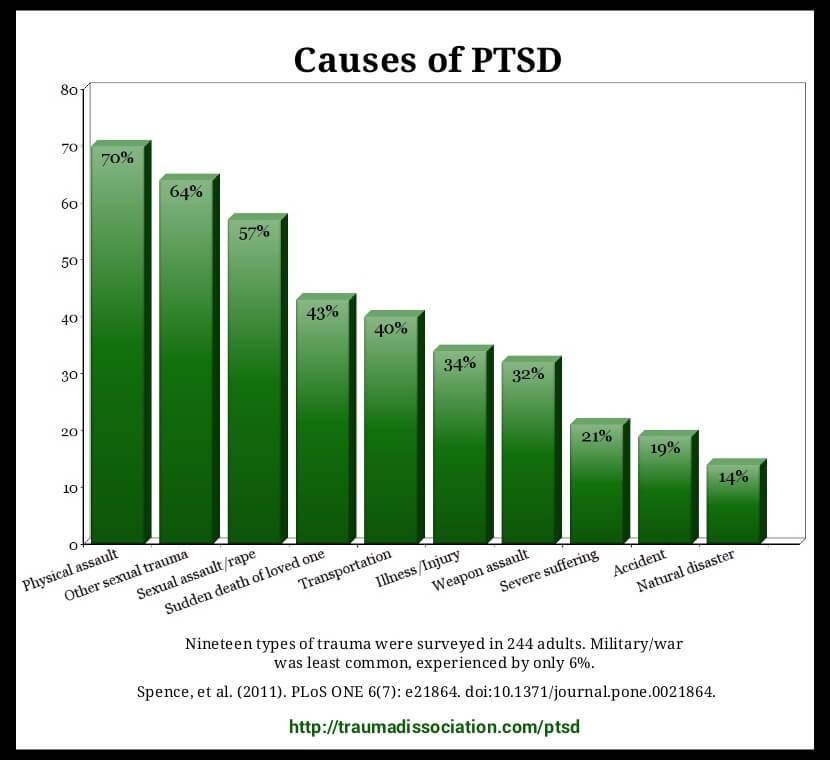
- Actual death of someone
- Threatened death
- Combat
- Survivors of sexual abuse
- Survivors of physical abuse and neglect
- Proximity
- Experienced by the patient
- Witnessed by the patient
- Told to the patient (especially when family members are exposed)
- Post-trauma presence - paramedics, firefighters, police officers...

- Disorder symptoms
- Intrusion
- Memories, flashbacks
- Mood changes
- [Almost always] Depressed mood
- Dissociation
- Depersonalization
- Avoidance
- Avoiding the location, people or conversations
- Arousal
- Hypervigilance
- Looking for danger
- Intrusion
- Diagnosis - designed to lower the number of false negatives
- Shorter than 1 month = Acute stress disorder
- Treatment at this stage very effective
- Longer than 1 month = PTSD
- Treatment more difficult
- Shorter than 1 month = Acute stress disorder
- Treatment
- Psychotherapy is the best - group therapy
- Can be problematic to some people who have developed avoidance
- Medical therapy
- Chronic
- SSRIs
- Acute - for panic attacks
- Benzodiazepines
- Chronic
- Psychotherapy is the best - group therapy
- Adjustment disorder

- Life-changing (non-life threatening) stressor leading to a disorder
- Mood changes can be present but no mood disorder is present
- There is no psychosis, suicidal ideation, homicidal ideation
- Diagnosis
- Onset within 3 months of the stressor
- Duration <6 months
- Treatment
- Medical - none
- Therapy may be helpful
- Reactive attachment disorder

- Little pairing with others
- Stressor
- Abuse or neglect in infancy
- Can be caused by parents or institutional care
- Learn to be lonely
- Mood disorders
- Substance addictions
- Learning disabilities
- Diagnosis
- Made <5 years
- Autism must be ruled out
- Treatment
- Very difficult
- Targeted at the caregiver
- Give them resources
- Replace caregivers
- Disinhibited social engagement disorder

- Too much pairing with others
- Stressor
- Abuse or neglect in infancy
- Can be caused by parents or institutional care
- No difference between strangers and friends
- Diagnosis
- Made <5 years
- Autism must be ruled out
- Treatment
- Very difficult
- Targeted at the caregiver
- Give them resources
- Replace caregivers
All information provided on this website is for educational purposes and does not constitute any medical advice. Please speak to you doctor before changing your diet, activity or medications.
